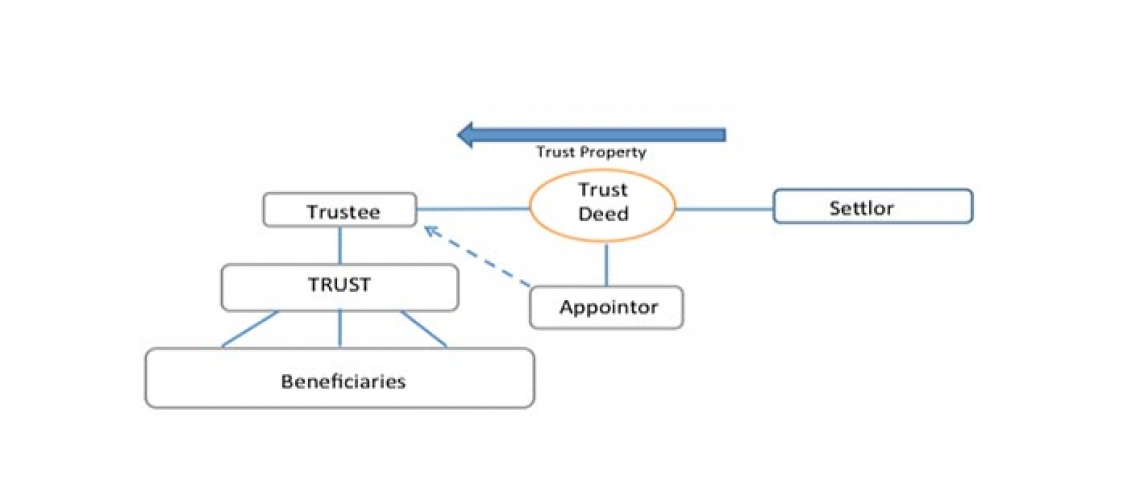
There are many types of trusts that are setup to protect financial assets and income from claims against the beneficiaries or trustee.
- Deceased estate trust
- Discretionary trust
- Fixed trust
- Fixed unit trust
- Hybrid trust
- Public unit trust – listed or unlisted
- Special disability trust
- Superannuation funds trust
- Charitable trust
- and many more
There are two main type of trusts which are commonly used in business and by individuals,
Discretionary or family trust
Discretionary trust or family trust is the most common structure used by families and in business. There is no defined entitlements to the income or the assets of the trust. Each year, the trustee has the full discretion on the amount of income distribution and which beneficiary to receive the portion of the income of the trust. For this reason, it has become popular in tax planning.
Fixed or unit trust
Under a fixed trust or unit trust, the beneficiaries have a defined entitlement under the trust which is similar to how shareholding works in a company. The trust is divided into units in the same way as a company shareholding is divided into shares. The trustee does not have any control or discretion on how to distribute the trust’s asset or income to the beneficiaries. It is often used by joint venture arrangement.
Does a trust pay tax?
A trust of all the above mentioned types are not liable to pay tax. The reason being a trust does not own the asset or income. Its income is distributed to the beneficiaries. The beneficiaries pay the tax rate based on their income tax level bracket. A trust has its own TFN. If a trust is used to conduct a business enterprise, it has its own ABN and if there is a need for GST, it will be register for GST.